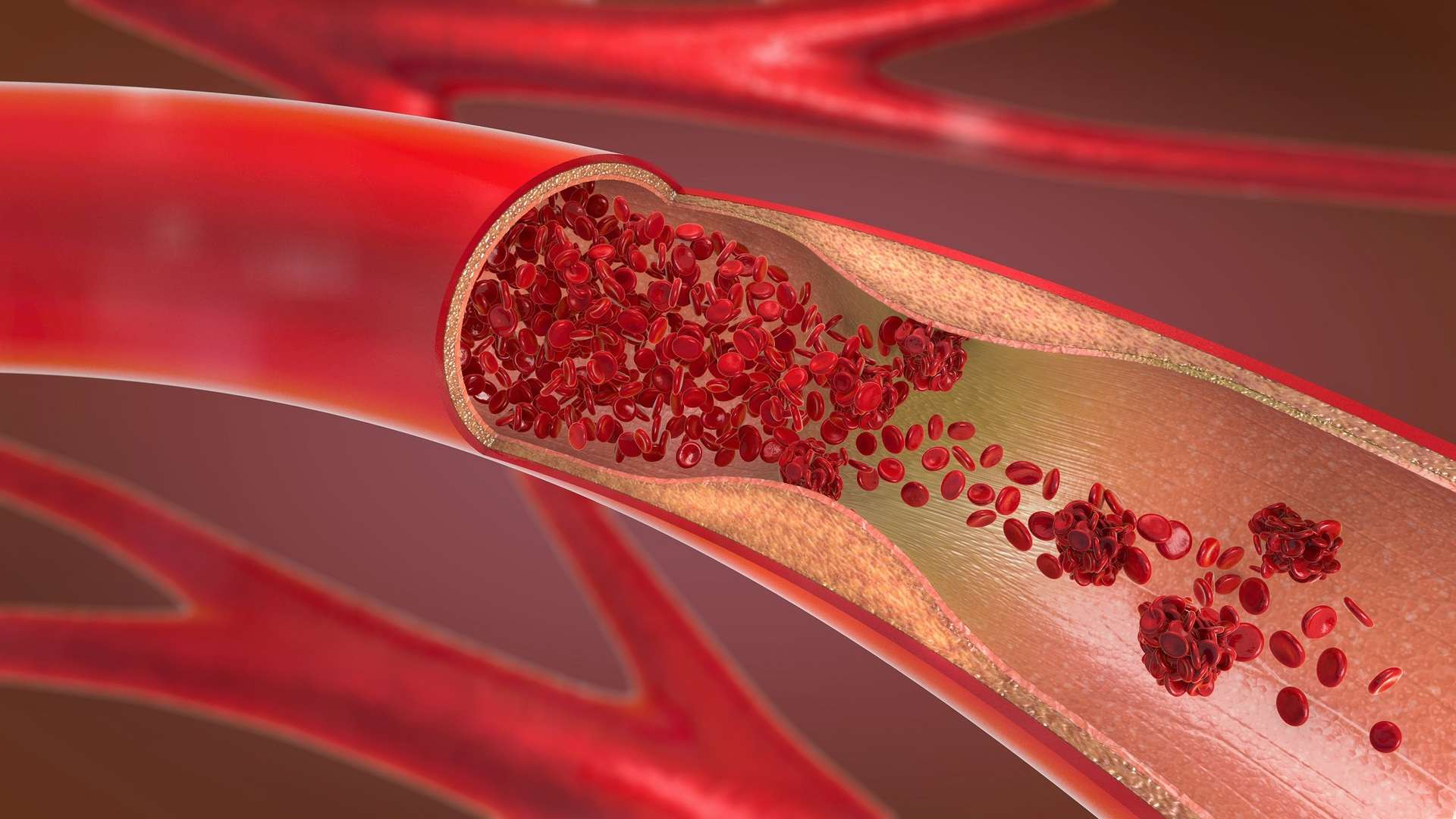
How can the risk of cardiovascular disease be reduced?
In principle, it is easier than you might think to prevent cardiovascular disease by adopting a healthy lifestyle. Prevention can be compared with protection against sunburn: If you put on sunscreen and get out of the sun in time, you protect your skin. And if you adopt a generally healthy lifestyle, you can prevent cardiovascular disease without having to make any special effort.
Three factors play a special role here: sufficient exercise, a balanced diet and good stress management.
Sufficient exercise
Humans are not made to sit a lot, have an abundance of food, and avoid exercise. In fact, a big factor in cardiovascular problems is lack of exercise.
Getting enough exercise is important for several reasons:
- Stamina: Good stamina means the body can withstand stress. Improving fitness therefore also strengthens the heart and lungs. Increased exertion requires the heart to pump faster and more vigorously to supply the body with oxygen. This targeted load trains the heart. Although the heart is called an organ, it is actually a muscle. Lung capacity also increases as a result of exercise: As a result, the lungs can oxygenate the blood faster and better.
- Removal: Pollutants and carbon dioxide are better removed from the blood and thus from the body during exercise. This sometimes prevents arterial deposits, which can be quite dangerous. Those who have problems with swollen ankles will notice something else: Exercise causes the body to break down lymphatic fluid that collects in the tissues of the lower legs and causes swelling. In particular, the work of the calf muscles is important for this.
- Weight: More calories are burned through exercise. At the same time, the body draws on stored fats to maintain energy levels. Exercise therefore basically helps to prevent obesity and reduce weight.
Those who engage in muscle-building sports are very less likely to lose weight and more likely to gain weight. This is not tragic in terms of the cardiovascular system. Muscle promotes the maintenance of a healthy body and burns many more calories than simple tissue, even at rest.