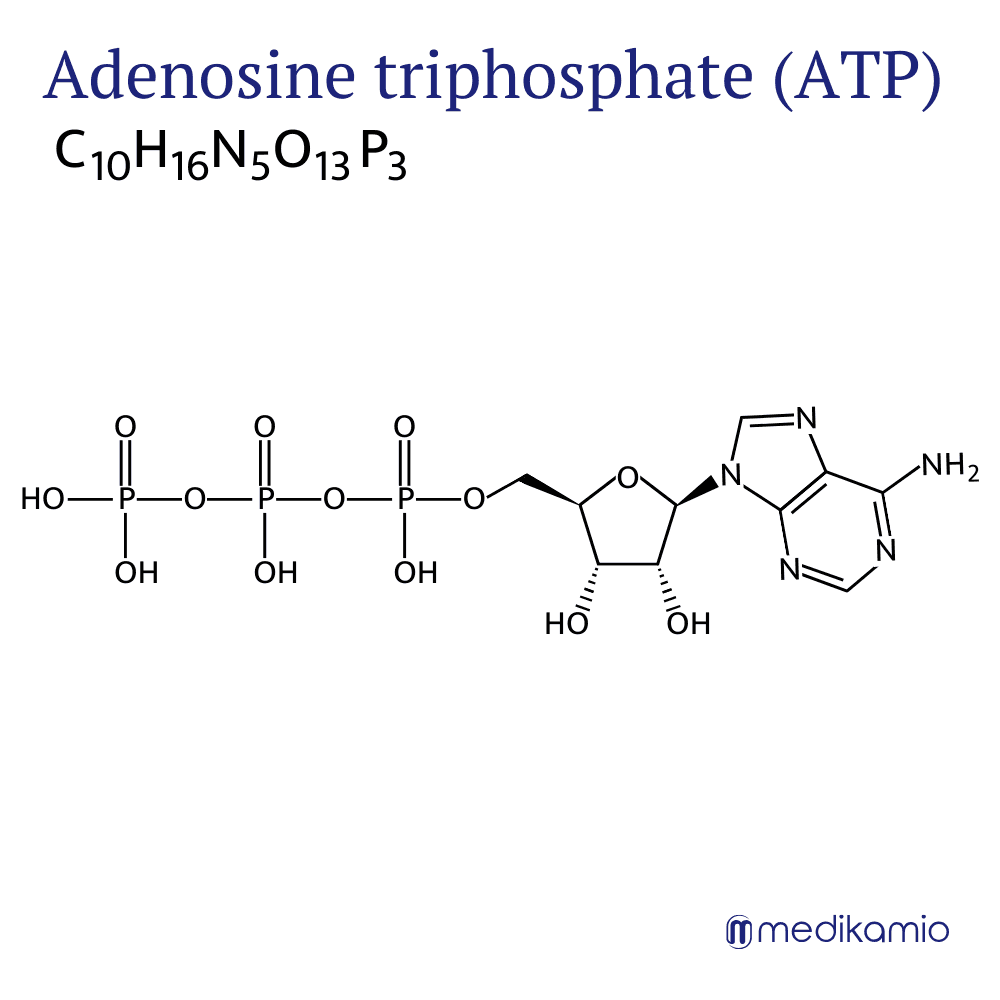
Basics
Adenosine triphosphate consists of three parts, namely the nucleic base adenine, the sugar ribose and three phosphates. They are covalently linked to each other. The combination of adenine and ribose is summarized in the name and thus results in adenosine. ATP is a universal energy carrier in all living organisms. The body needs it for many biochemical processes, including the transport of substances, the production of molecules, movement processes, muscle contraction, signal transmission and much more. The splitting of the phosphate groups and the subsequent addition of water, also known as hydrolysis, releases biochemical binding energy that can be used by the body. Pharmaceutically, adenosine triphosphate can be used to dilate blood vessels (vasodilation).