Basics
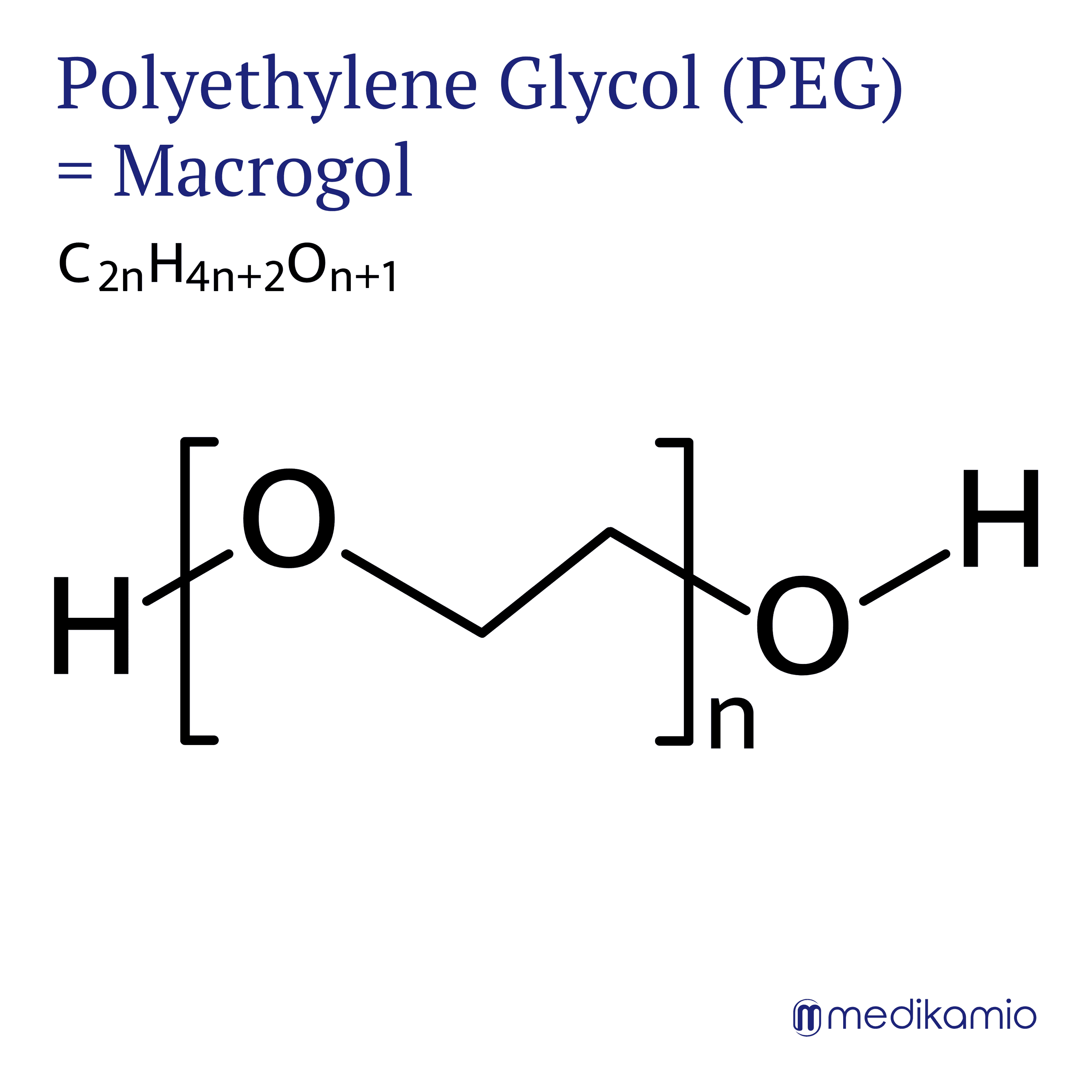
Macrogol, also known as polyethylene glycol (PEG), is a laxative that forms its own group, the macrogols. There are many different macrogols, all with a number as an epithet indicating their molecular weight. The best known are macrogol 3350 and macrogol 4000. Macrogol is used to treat constipation and to empty the bowels. Due to its ability to bind water, the stool becomes more fluid and thus has a laxative effect. Macrogol is not metabolized or absorbed. Macrogol is often used in medicines in combination with salts such as potassium chloride or sodium chloride. Macrogols are linear and therefore form very long chains. Depending on the molecular mass, macrogol is a viscous liquid (200-400 g/mol) or a white solid substance (>3000 g/mol). Due to its many oxygen atoms, polyethylene glycol is highly soluble in water. Macrogol can also be used before colonoscopies to empty the bowel.