Basics
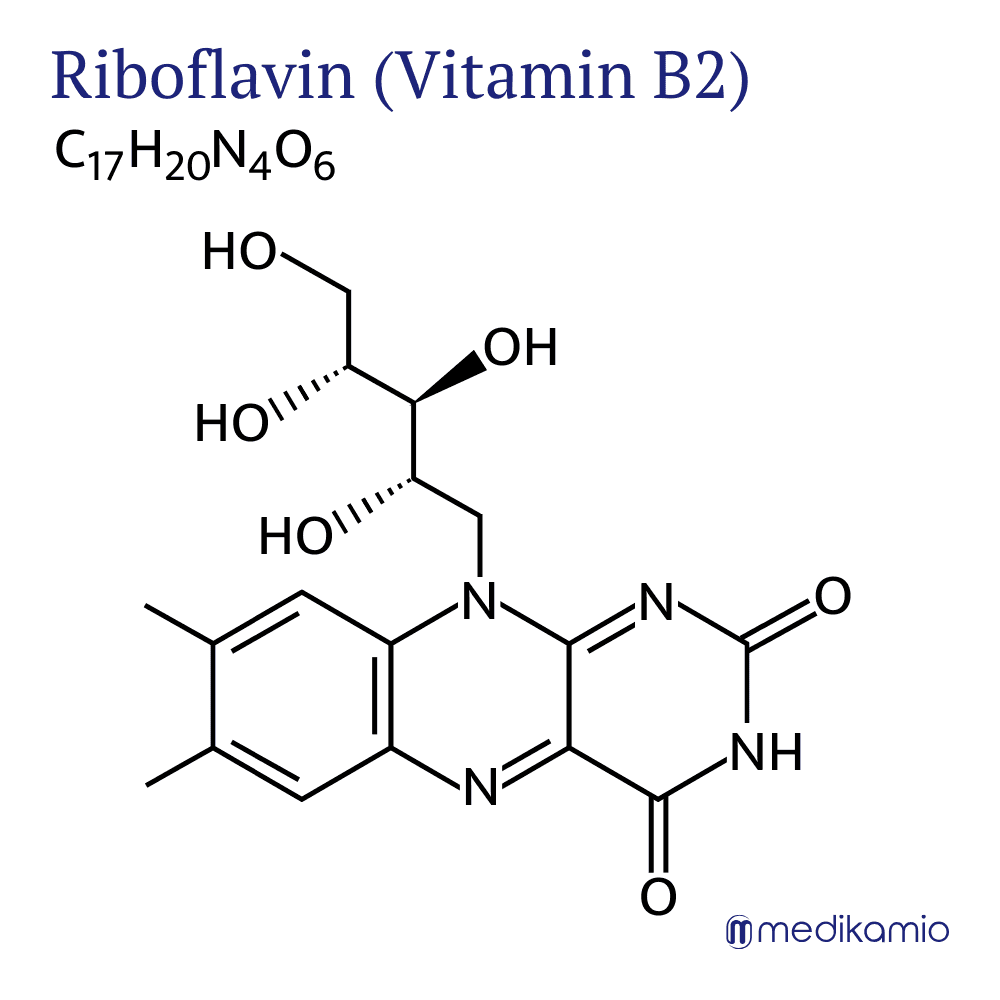
Riboflavin is an active ingredient for the prevention and treatment of vitamin B2 deficiency. It belongs to the group of B vitamins and is important for many metabolic processes in our body. Among other things, the active ingredient is involved in the formation of red blood cells, respiration, antibody production, growth and reproduction. Riboflavin is a prodrug and is first converted in the body to FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide) and FMN (flavin mononucleotide), which are active as cofactors in many enzymes. A prodrug is an inactive substance that is only converted into its active form in the body, where it is supposed to work. Vitamin B2 is contained in many foods and is almost exclusively available as a combination preparation in medicines. As a vitamin supplement, it ensures healthy skin and nails, regulates the activity of the thyroid gland and prevents eye diseases such as cataracts. The vitamin B2 requirement is mainly covered by dairy products. Riboflavin is a yellow to orange powder that tastes bitter and is soluble in water. When taking the active ingredient, it should be noted that the urine can turn a very intense yellow color, but this is not dangerous. Riboflavin is light-sensitive but heat-resistant.