Basics
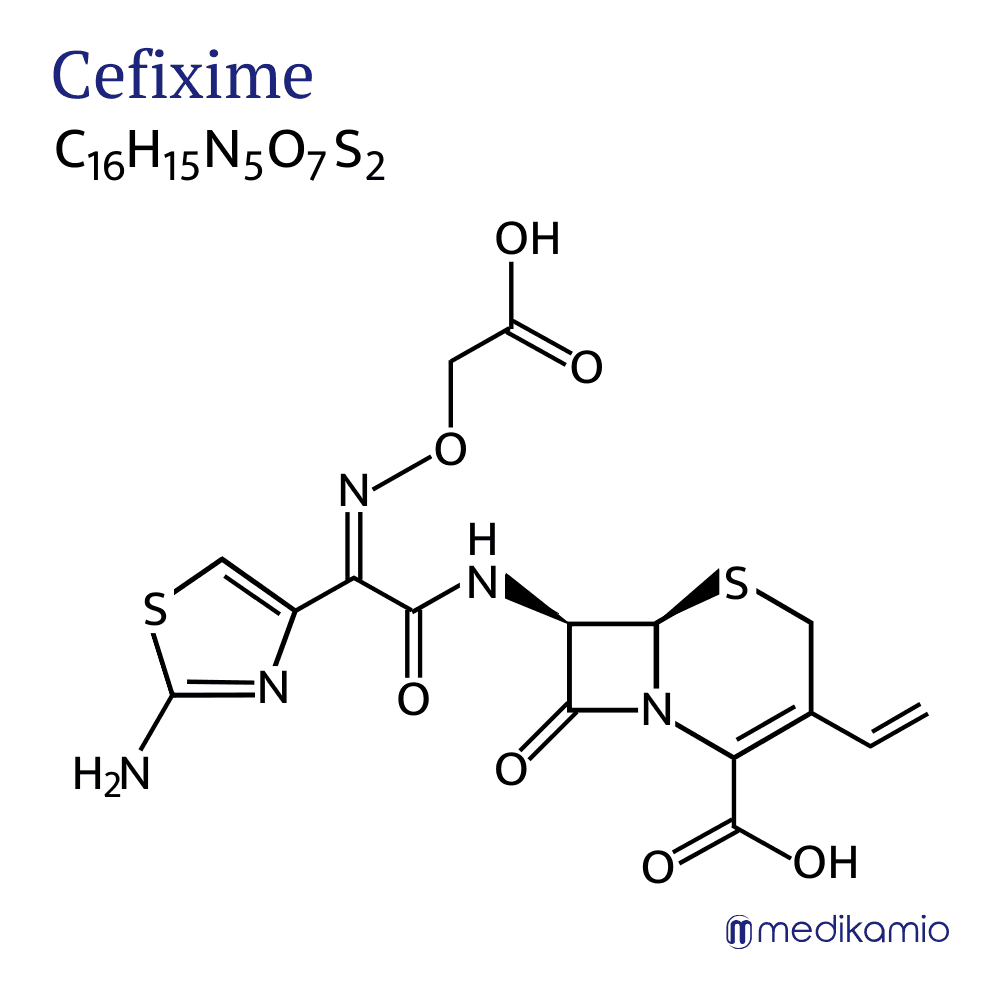
Cefixime is an active substance for the treatment of bacterial infections. It belongs to the group of cephalosporins, a class of antibiotics. Cephalosporins are broad-spectrum antibiotics and are part of the ß-lactam antibiotics. Cefixime is mainly used to treat respiratory diseases, urinary tract infections and gonorrhea. Like the other representatives of the cephalosporins, cefixime has the functional group of a cephem. It is a white powder that is slightly soluble in water. The active ingredient is available in several different forms, as tablets, film-coated tablets, dry juice or granules. It occurs naturally in the mold Cephalosporium acremonium.