Basics
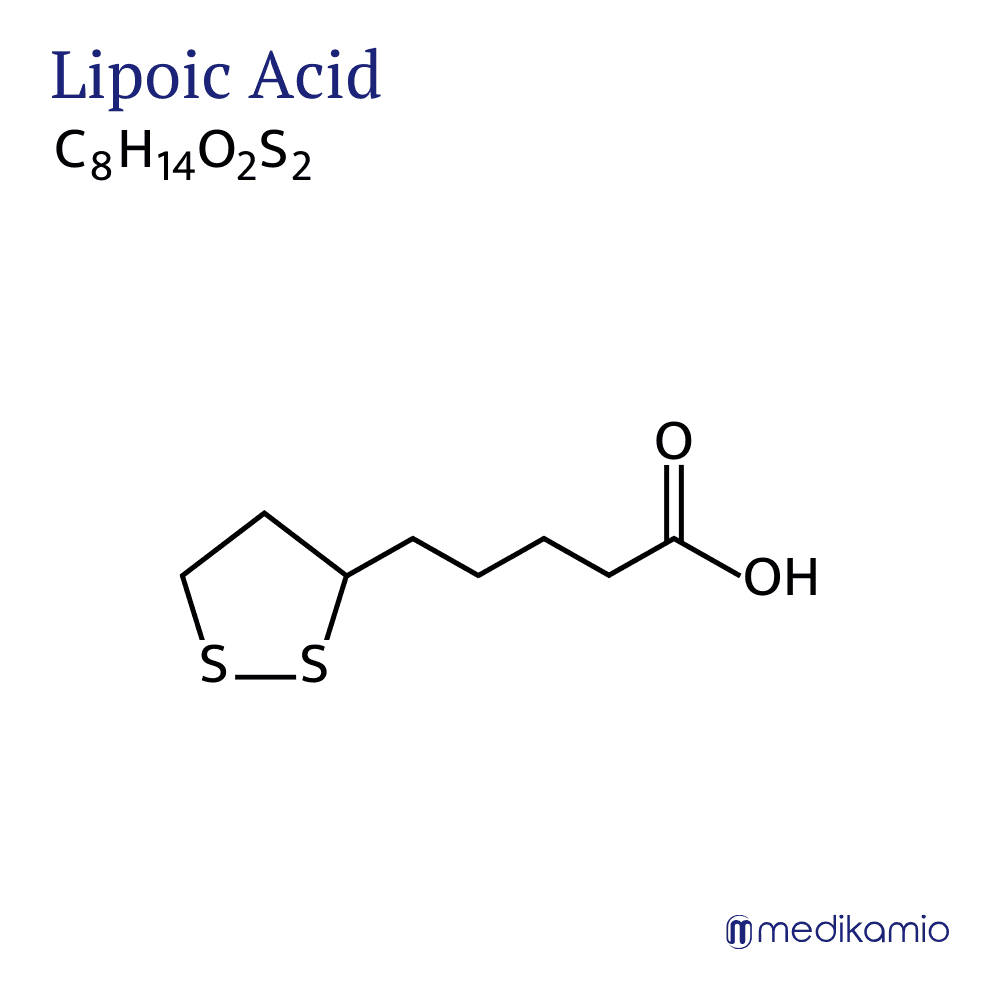
Thioctic acid or alpha-lipoic acid is an active ingredient that is used for the supportive treatment of diabetic polyneuropathy, for the treatment of heavy metal poisoning and as a dietary supplement to promote healthy liver function. It is a sulphur-containing fatty acid. The two sulphur atoms can form disulphide bridges in oxidized form. Thioctic acid is a racemate. A racemate is an active substance that consists of 2 molecules that occur in a 1:1 ratio and behave like image and mirror image. One speaks of the R-(dextrorotatory) enantiomer and S-(levorotatory) enantiomer. Enantiomers do NOT differ in their physical properties such as melting or boiling point. However, they can have the opposite effect. For example, (S)-carvone smells like caraway and (R)-carvone smells like mint. The amino acid (S)-valine tastes bitter, while (R)-valine tastes sweet. For these reasons, both enantiomers are always tested in today's approval procedures for new active ingredients. Sometimes one enantiomer can be converted into the other in the body.