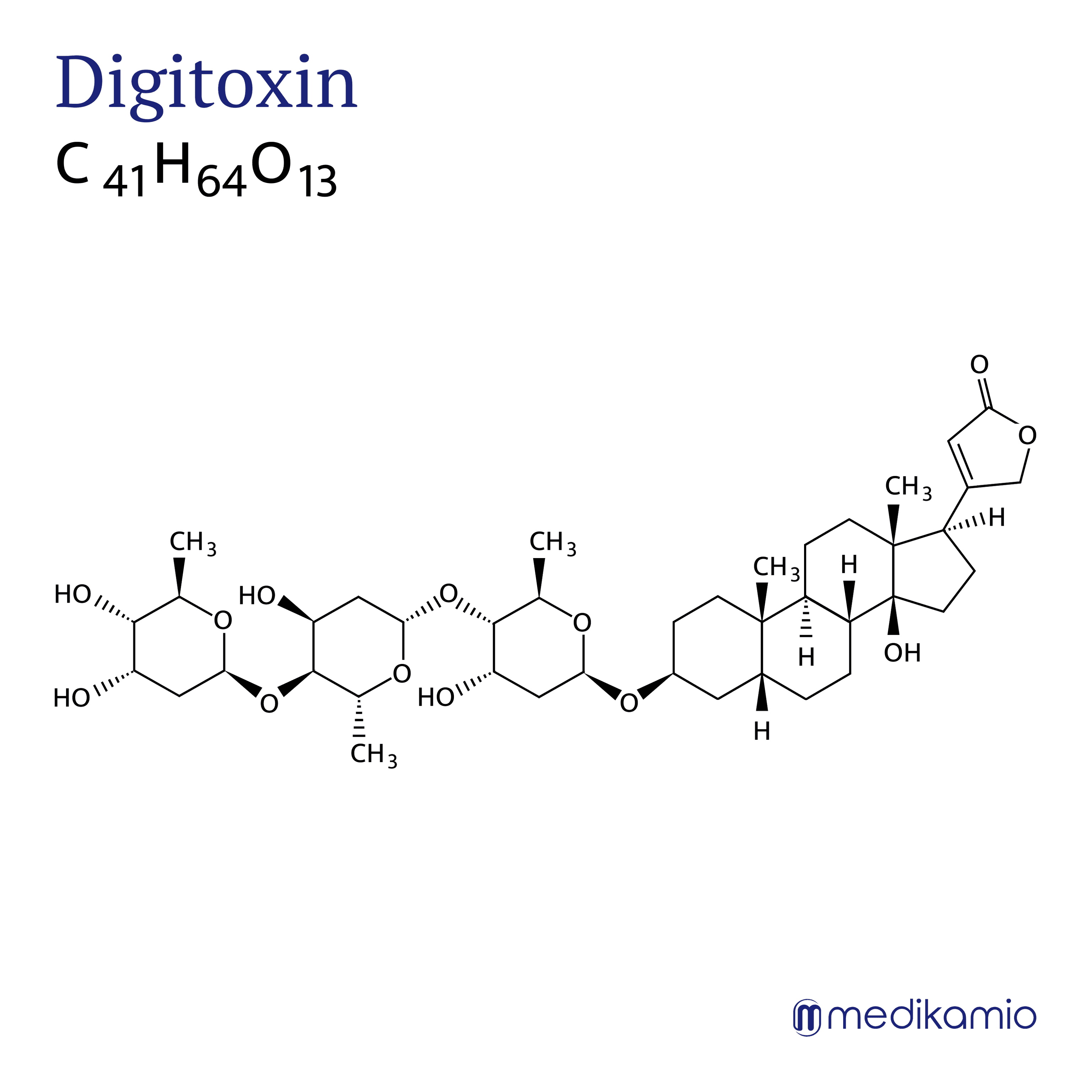
Basics
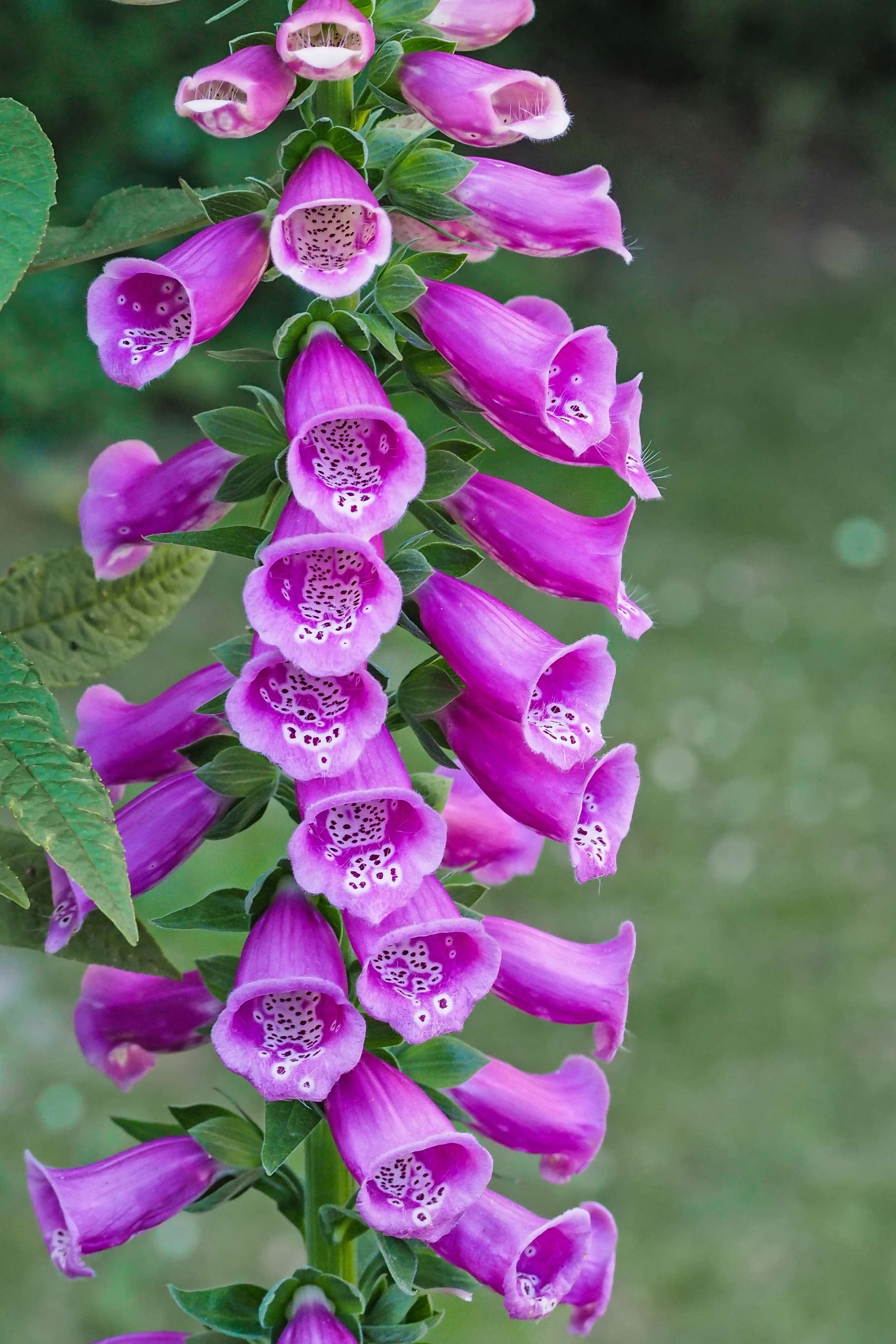
Digitoxin is an active substance used to treat chronic heart failure, cardiac arrhythmias and muscular, accommodative (adaptive) or nervous eye fatigue. Digitoxin is a white powder that is insoluble in water. Digitoxin is a natural herbal ingredient from the red foxglove (Digitalis purpurea), which is native to Austria. Digitoxin belongs to the group of cardiac glycosides. Digitoxin is nowadays replaced by other therapies (with ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, diuretics) and is only rarely used. However, it is still used more frequently, especially in ophthalmology.