Basics
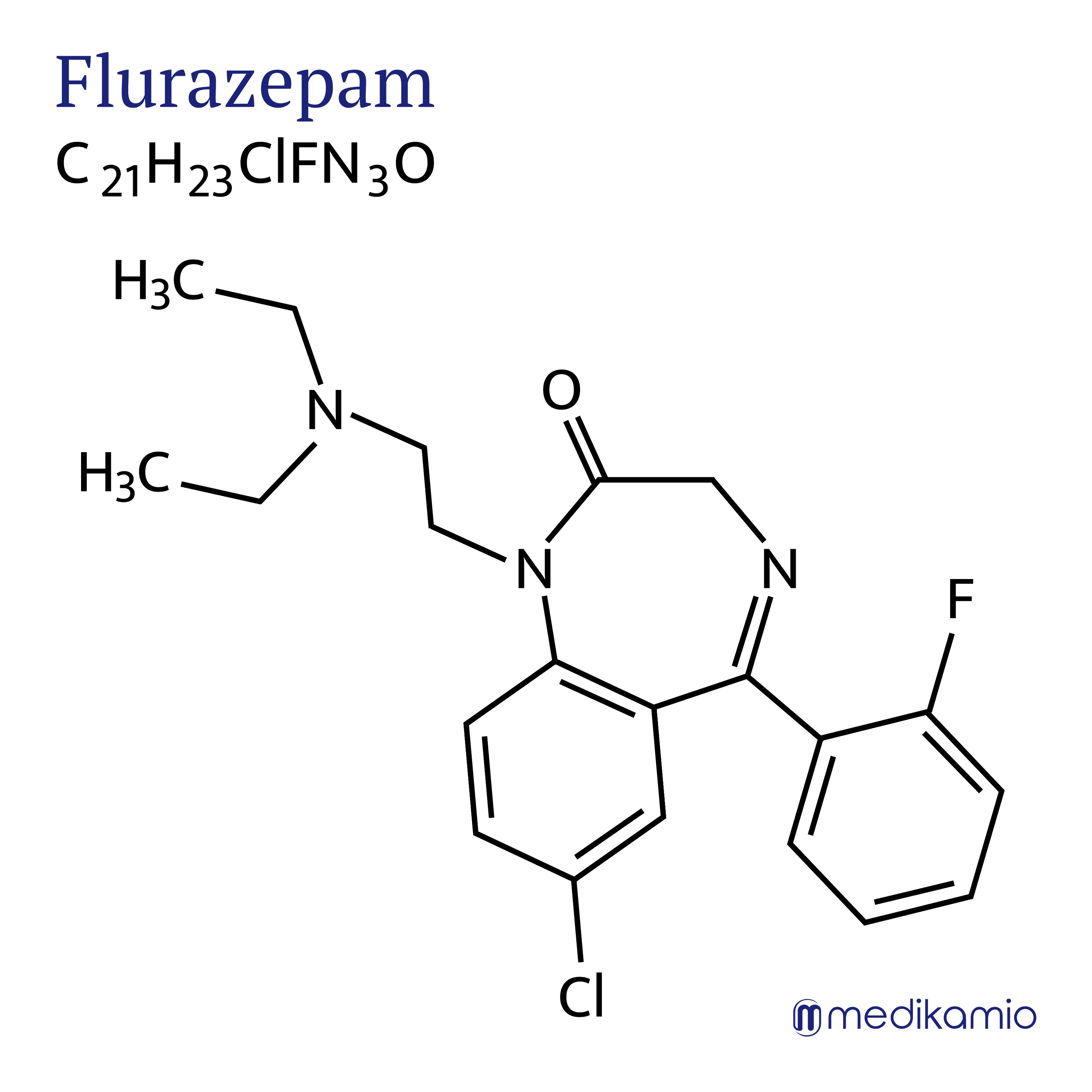
Flurazepam is an active ingredient that is used to treat sleep disorders. It belongs to the group of benzodiazepines, which have a calming and sleep-promoting effect. Flurazepam is a long-acting benzodiazepine. It has a rapid onset of action and is based on binding to the GABA receptors. Like all other benzodiazepines, flurazepam can also be addictive. Flurazepam is also often abused as a narcotic. It is usually present in medicines as flurazepam hydrochloride. It is white, crystalline and very easily soluble in water. Dream times remain unaffected when taking flurazepam.